Apache Airflow's Task Lifecycle and Architecture
Hi, I am coder2j.
In this tutorial, I will guide you through the task life cycle and basic architecture of Apache Airflow.
By the end of this, you’ll have a solid understanding of how tasks progress from initiation to completion and how the core components of Airflow collaborate.
If you are a video person, check out the YouTube video.
Let’s dive right in!
Task Life Cycle #
Let’s start by exploring the life cycle of an Apache Airflow task. Tasks undergo various stages, each denoting a specific status.

There are a total of 11 stages, visualized by distinct colors in the Airflow UI (graph and tree views).
No Status to Queued #
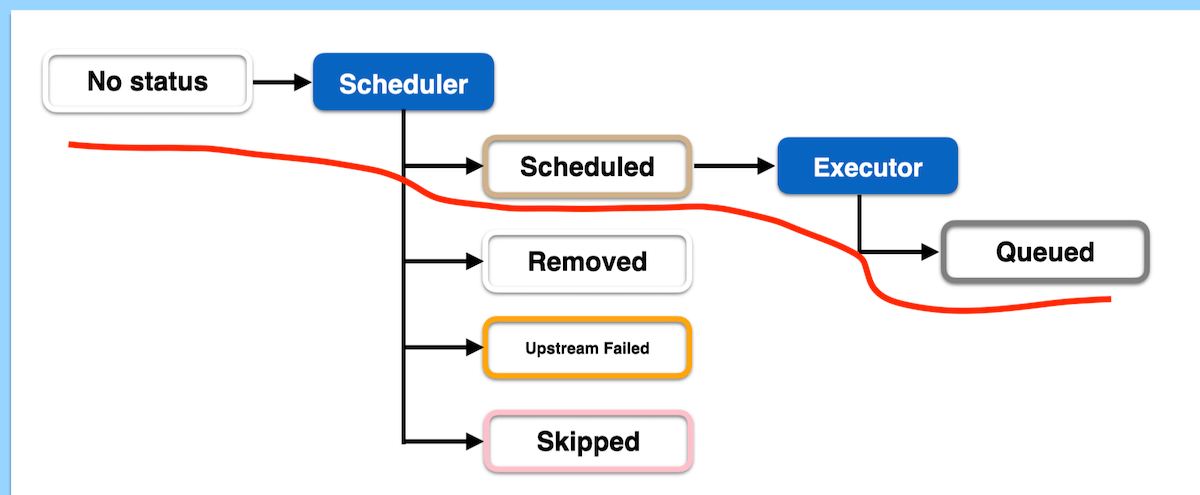
- The task begins with no status, indicating the scheduler has created an empty task instance.
- If fortunate, the task moves to the
queuedstage as the executor puts it in the task queue.
Running to Success (or Failed/Shut Down) #
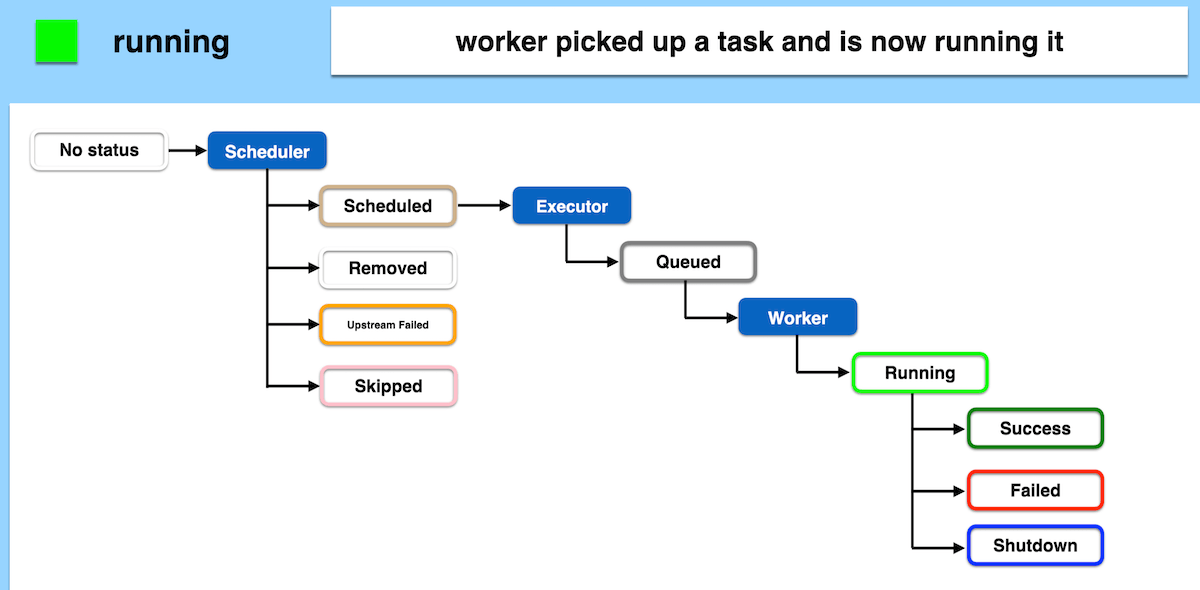
- The worker executes the task, changing its status to “running.”
- Depending on the outcome, the task may transition to “success,” “failed,” or “shutdown.”
Retry and Reschedule #
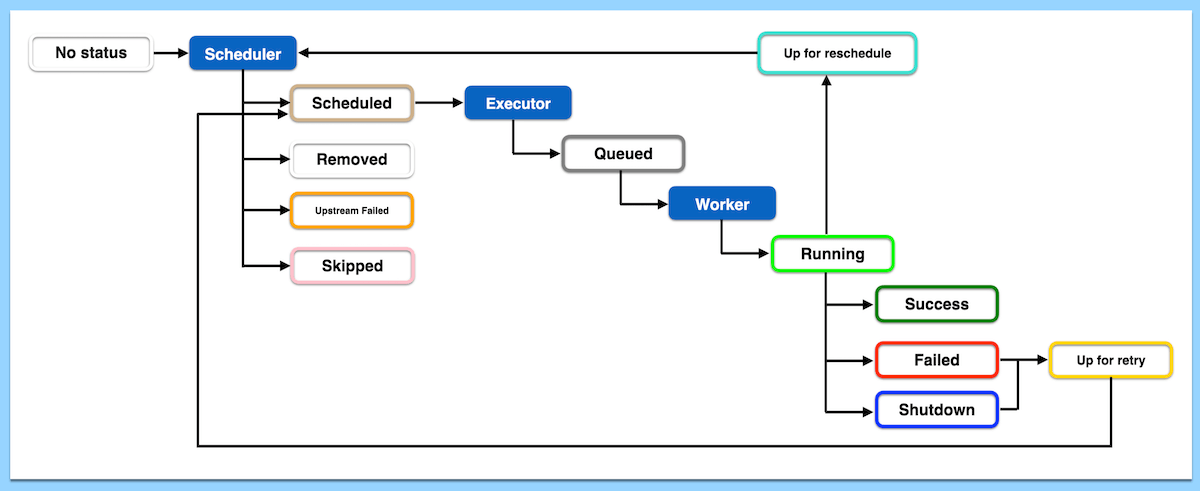
- In case of failure or shutdown, and if the maximum retry is not exceeded, the task may go to the “up for retry” stage.
- Additionally, tasks in the running stage might be directed to the “up for reschedule” stage for periodic reruns.
Happy Workflow Execution Process #
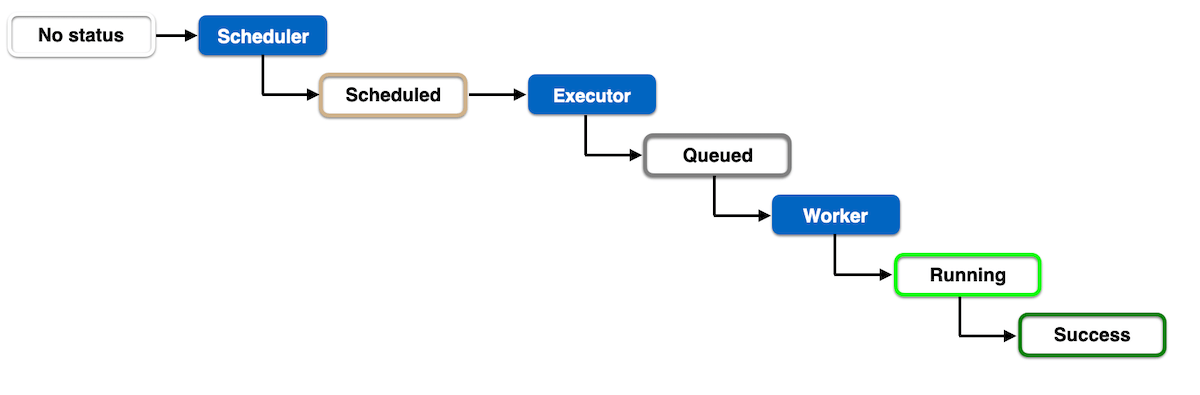 In summary, a smooth workflow involves starting with no status, scheduling the task, queuing it for execution, flawless execution, and concluding with a successful task process.
In summary, a smooth workflow involves starting with no status, scheduling the task, queuing it for execution, flawless execution, and concluding with a successful task process.
Basic Architecture of Apache Airflow #
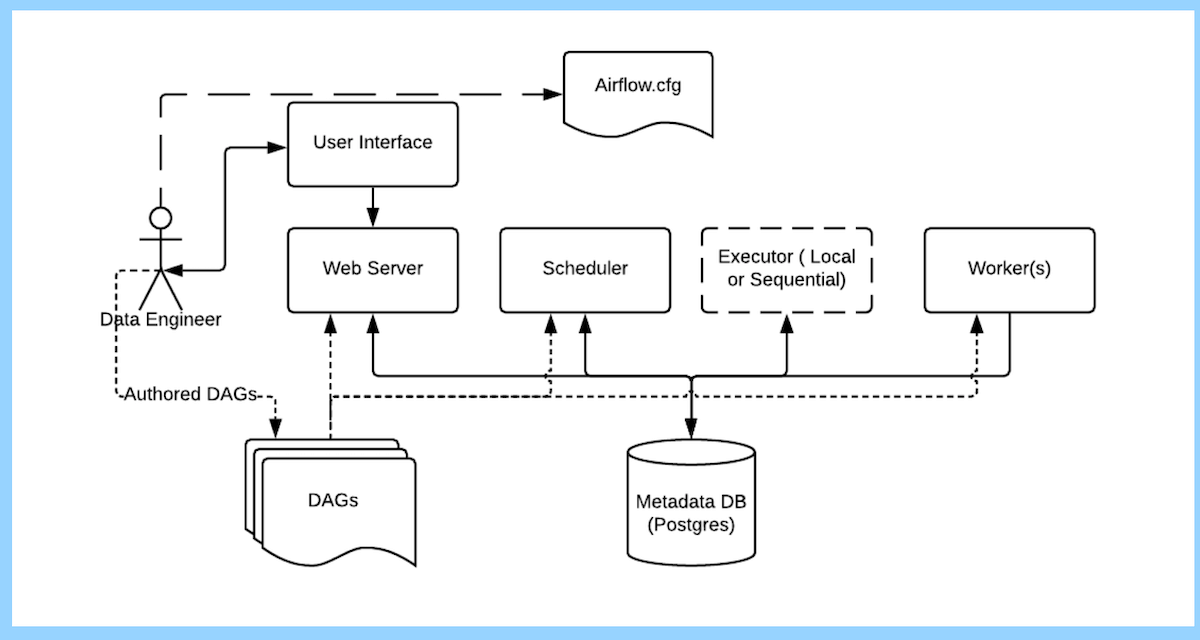
Now that we understand the task life cycle, let’s explore the fundamental architecture of Apache Airflow. The following are the main components:
-
Data Engineer:
- Responsible for building and monitoring ETL processes.
- Configures Airflow settings, such as the executor type and database choice.
- Manages DAGs through the Airflow UI.
-
Web Server, Scheduler, and Worker:
- The web server supports the Airflow UI, visible to data engineers.
- The scheduler manages DAG visibility and influences task status.
- Workers execute tasks picked from the queue.
- Database and Executor:
- Connected components for persisting DAG updates and information retrieval.
- Various database engines like MySQL or PostgreSQL can be chosen.
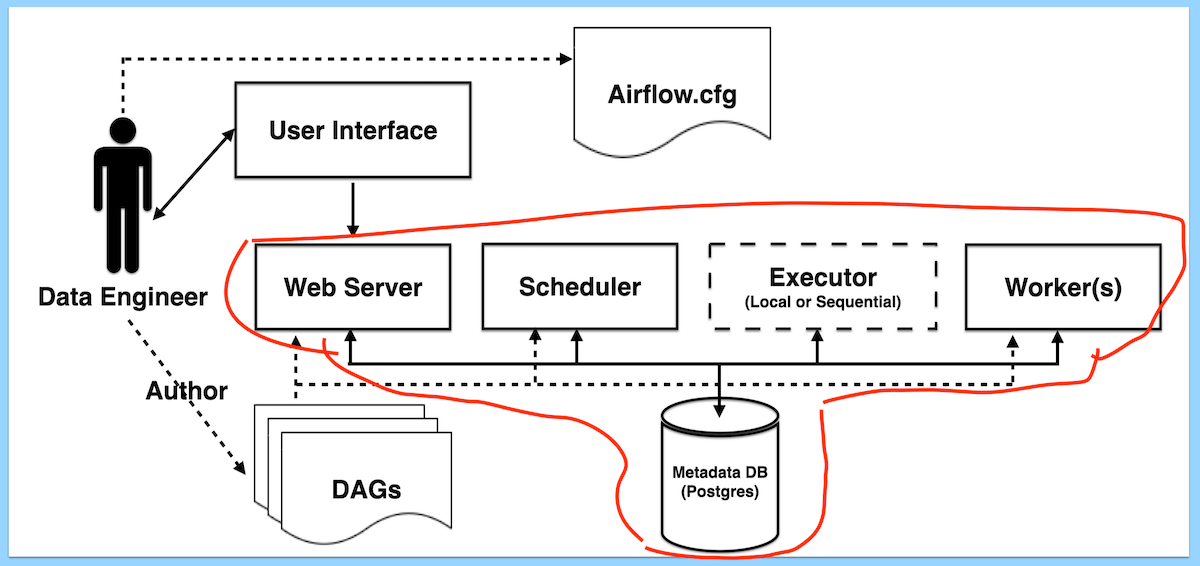
And there you have it - a comprehensive guide to Apache Airflow’s task life cycle and basic architecture. I hope you’ve enjoyed this tutorial!
Now, it’s your turn. Do I miss anything for you to understand the Airflow task life cycle and architecture?
Let me know if you face any issues or any suggestions in the comment below.
Related Posts

Comments: